Anaplastic astrocytoma of the brain
The content of the article
Astrocytomas account for half of all neoplasms of the central nervous system, among which anaplastic astrocytoma of the brain is one of the most dangerous, as it is characterized by a malignant nature. It is noteworthy that in the stronger half of humanity, these diseases occur much more often than in women. Malignant tumors are mainly diagnosed in patients over 40. As for children, piloid astrocytoma is more common in them.
Astrocytomas are neuroepithelial neoplasms of the brain that arise from astrocyte cells. The latter are cells of the central nervous system and perform a supporting and restrictive function. It is customary to distinguish two types of cells: protoplasmic and fibrous. The former are localized in the gray matter of the brain, and the latter in the white matter. They take an active part in the transfer of substances between blood vessels and nerve cells, and also envelop capillaries and neurons.
Types of astrocytic diseases
All tumors of the central nervous system are divided according to the international histological classification. As for astrocytic diseases, the following types can be distinguished:
- Astrocytoma: large cell, fibrillary protoplasmic astrocytoma;
- Anaplastic astrocytoma prognosis is complete recovery, which depends on the success of removal of the primary lesion;
- Glioblastoma: gliosarcoma and giant cell glioblastoma;
- Pilocytic astrocytoma;
- Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma;
- Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma. According to the nature of their development, astrocytomas are divided into the following types:
- Nodal growth. These include piloid cerebral astrocytoma, pleomorphic and subependymal giant cell astrocytoma.
Such astrocytomas are characterized by a growth node and clearly defined boundaries that are separated from the surrounding brain tissue.
As for pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma, it is quite rare, and if diagnosed, it is more often in patients at a young age. It develops in the form of a node in the cerebral cortex, and may be distinguished by the presence of a cyst. Becomes the cause of epileptic seizures.
Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma is most often localized in the ventricular system of the brain.
Diffuse growth: this includes benign astrocytoma, glioblastoma, and anaplastic astrocytoma, with diffuse astrocytoma classified as grade 2 malignancy.
Astrocytomas, which are characterized by diffuse growth, do not have clear boundaries with brain tissue, as they can grow strongly into the medulla and reach very large sizes. In this case, benign astrocytoma degenerates into malignant in 70% of cases.
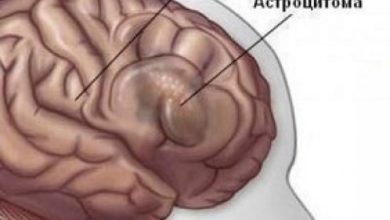
Anaplastic astrocytoma is immediately distinguished by its malignant nature. As for glioblastoma, it is a highly malignant neoplasm that is characterized by rapid growth. Most often localized in the temporal lobes.
Causes of the disease
Experts say the main cause of astrocytoma is the malfunction of genes that should prevent the development of tumors. Patients diagnosed with astrocytoma are diagnosed with a “breakdown” of the TP53 gene.
The risk group also includes those whose immediate blood relatives suffered from similar tumors. This group includes workers at oil refineries, as well as those who have dealt with radiation or are carriers of oncogenic viruses.
To date, experts have not precisely studied the reasons that cause the formation of brain tumors, as well as provoke their growth. As is the case with other oncological diseases, experts note the complex impact of several negative factors, which are the cause of the formation of a brain tumor.
Symptoms
The main feature of this disease, like other brain tumors, is that they are localized in a closed space of the skull, and therefore sooner or later lead to damage to both nearby and distant brain structures. In the first case, focal symptoms will appear, and in the second, secondary symptoms.
Primary symptoms
If the tumor affects the frontal lobe, the patient may experience a feeling of euphoria, begins to ignore his problem or does not take it seriously, increased aggressiveness appears, as well as complete destruction of the psyche. When the tumor affects the medial surface of the frontal lobe or damages the corpus callosum, disturbances in thought processes and a significant decrease in memory are observed. If Broca's area is damaged in the frontal lobe, speech disturbances may occur, as a result of which the articulation of words is significantly reduced and speech becomes slower. The anterior parts of the frontal part are “silent”, and therefore, if they are affected by a tumor, symptoms may be completely absent for a long time. When the tumor affects the posterior sections, it leads to general muscle weakness and partial paralysis of the limbs.
Temporal lobe
When an astrocytoma is localized in this area, the patient begins to suffer from hallucinations, both visual and auditory. In the future, this problem can develop into the occurrence of epileptic seizures. If the tumor affects the temporal lobe of the dominant hemisphere, the patient may no longer understand oral and written speech, and his speech will consist of a set of arbitrary words. A symptom that often appears is auditory agnosia - this is the failure to recognize voices, melodies and sounds that the patient previously knew. Very often, with astrocytoma of the temporal region, a person dies without even starting treatment.
Most often, epileptic seizures occur with astrocytomas, which are localized in the frontal and temporal lobe:
- Uncontrollable turns of the head may occur, as well as periodic spasms in the limbs;
- The patient complains of a feeling of “crawling goosebumps” on the skin, and objects may begin to change their color;
- Increased nausea and cardiac dysfunction;
- Sometimes cramps begin in one part of the body and gradually spread to another part;
- Severe partial seizures may occur when the patient’s consciousness is disrupted, he stops making any contact with others, begins to repeat the same sounds and even sing;
- A person may “freeze” for a few seconds, after which he returns to normal activities.
Parietal lobe
If a tumor affects this lobe, the patient may no longer recognize objects by touch, and apraxia of the hand may also occur, in which the patient cannot fasten buttons, put on clothes, etc. In this case, epileptic seizures are also typical. When the left parietal lobe is damaged, the patient is impaired in writing, speaking and counting.
Occipital lobe
In this area, astrocytomas are the least common. Usually accompanied by visual hallucinations, and one half of the picture may fall out of each eye.
Secondary symptoms of this disease include the following:
- Headache . Astrocytoma begins to resemble itself precisely with headaches and epileptic seizures. Headache is associated with intracranial hypertension, and is characterized by unclear localization of the source of pain. Initially, the pain may be periodic and aching. As the tumor grows, the pain may become constant. Most often occurs when changing body position. Suspicion of its formation should arise if the headache appears after sleep and decreases slightly in the evening, and may be accompanied by an increased gag reflex, which is not associated with food intake;
- Brain swelling. The tumor, which as it grows begins to compress the cerebrospinal fluid pathways and other parts of the brain, causes increased intracranial pressure.
It manifests itself as severe headaches, nausea, vomiting, frequent hiccups, impaired memory and thought processes, decreased vision, etc.
Diagnostics
There are several diagnostic methods that can not only detect the formation of a tumor in the brain, but also recognize its stage. These include the following diagnostic principles:
- Tomography
It is divided into several subtypes, thanks to which specialists are able to diagnose astrocytoma:
- MRI . It is one of the most accurate studies. Thanks to MRI, the specialist is able to recognize the degree of malignancy of the formation;
- CT. This method is carried out on the basis of radiology and produces a layer-by-layer image of brain structures. This allows you to diagnose the specific location of the tumor, as well as its structure;
- PAT. Before the diagnosis begins, a dose of radioactive glucose is injected into the patient's vein. It is an indicator, thanks to which it is possible to detect the exact location of the tumor. Thanks to this method, the specialist will also be able to find out about the effectiveness of the chosen treatment.
- Biopsy
- Angiography
The peculiarity of this method is the introduction of a special dye, thanks to which it is possible to identify the vessels that feed the tumor tissues. This method allows the specialist to more accurately predict future surgery.
- Neurological examination
It is more of an auxiliary method for tumor research. It allows you to check the correctness of the patient’s brain reflexes.
Stages of the disease
The generally accepted classification divides astrocytoma into four stages.
- Stage one - cerebellar pilocytic astrocytoma or pilocytic astrocytoma; complete recovery depends on the prompt intervention of a specialist. The disease is benign in nature. It is worth noting that if you do not seek help in a timely manner, the risk of degeneration into malignant disease increases to 70%;
- Stage two - fibrillary astrocytoma of the brain. It is also benign in nature, but in the case of fibrillary prostoplasmic astrocytoma, its treatment and prognosis can only be favorable if the tumor was diagnosed at an early stage, which made it possible to quickly move on to its treatment. It is worth noting that in the case of prompt initiation of treatment when diagnosing a tumor such as grade 2 brain astrocytoma, the prognosis for the patient will be favorable;
- Stage three is anaplastic astrocytoma of the brain, the life prognosis of which also depends on the surgical intervention of a specialist. The tumor develops very quickly, thereby affecting healthy cells, which often leads to the fourth stage - glioblastoma.
Treatment
Based on a study of the patient’s general condition, he is prescribed one of the treatment methods. The stage of development of the disease is also taken into account.
- Surgical intervention. Benign astrocytoma can be cured with surgery. However, tumor resection is not always necessary, so in some cases the patient may be prescribed radiation therapy. In the early stages, it does not always prove to be effective, so its use may be delayed until new symptoms appear.
Highly malignant astrocytomas cannot be completely cured surgically, so the patient is prescribed additional treatment that will kill the tumor cells. As additional measures, radiotherapy or chemotherapy may be prescribed. If it is not possible to completely eliminate the tumor, then the specialist’s goal is to reduce its size.
- Radiation therapy . Using this method, benign astrocytoma and malignant tumors can be cured. A clearly directed radiation beam is used that does not damage healthy tissue.
This procedure is carried out in two ways:
- Internal influence. In this case, radioactive substances are injected into the damaged tissue; External influence. The source of radiation is outside the body.
- Chemotherapy . This method involves giving the patient drugs that can kill cancer cells.
- Radiosurgery. This method involves the direct effect of radio radiation on tumor cells. The peculiarity lies in accurate computer calculations before the start of the procedure. This allows the beams to be directed specifically to the tumor area, which eliminates damage to healthy tissue.
Prognosis and life expectancy
Unfortunately, brain astrocytoma is a serious disease and has adverse consequences. As practice shows, when diagnosed with grade 3 astrocytoma, survival does not exceed two to three years.
A specialist can establish an accurate forecast only by referring to the following points:
- Patient's age;
- The degree of malignancy of the tumor in the brain;
- Localization of the tumor;
- The rate of tumor development and damage to healthy tissues;
- Number of relapses.
Based on the information received, the specialist makes an approximate verdict. Patients are often interested in the question: if a benign astrocytoma is diagnosed, how long do they live with it? It is quite difficult to answer the question accurately, but for the first stage of the disease, experts predict no more than 10 years.
If a benign tumor transforms into a malignant one, the patient’s life expectancy is significantly reduced. When a tumor is diagnosed at the second stage, life expectancy can be reduced to 7-5 years, at the third stage - up to 3-4 years, and at the last stage the patient can live no more than a year and only if the clinical picture is positive.
Consequences
Based on the fact that serious methods are used to treat this tumor, and astrocytoma itself has a detrimental effect on the body, the consequences can be very negative.
Often patients may complain of blurred vision, even loss of vision. In some cases, a specialist may prescribe a course of rehabilitation measures that will be aimed at partially restoring vision.
After treatment for cerebral astrocytoma, the following complications may occur:
- Impairments in motor and support functions appear. In some cases, the patient may spend the rest of his life in a wheelchair;
- Speech is impaired;
- There is a disorder of the nerve endings that are responsible for perception, taste buds, etc.
Some patients do not disdain traditional medicine. Before treatment with folk remedies, you must consult a specialist. Otherwise, you can not only harm your body, but also significantly aggravate the situation with the active development of brain tumors. As for preventive methods for astrocytoma, they practically do not exist. The most important thing is to lead a healthy lifestyle and undergo regular examinations.
Please rate the article:

 (2 ratings, average: 4,50 out of 5)
(2 ratings, average: 4,50 out of 5)