Fibrillary astrocytoma
The content of the article
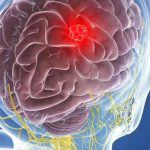
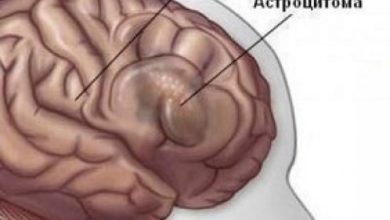
It can be localized from the optic nerve fibers to the cerebellum. In the early stages of the disease, astrocytes are structurally similar to healthy brain cells, without tissue necrosis and vascular atypia. During the growth of fibrillary astrocytoma, a cyst may form inside the tumor node. The pathological focus is non-aggressive, growth is usually slow, and the boundaries of the tumor are blurred. In rare cases, fibrillary astrocytoma can develop into a malignant form of formation - anaplastic, capable of metastasizing. It occurs in patients of different age groups, more often after 35 years.
Causes
The causes of this cancer have not been fully studied. The disease does not have a gender or clearly defined age characteristic. Risk factors include:
- Radioactive training – both production features and treatment option;
- Heredity;
- Previously suffered oncological diseases;
- Contact with carcinogenic substances;
- Weakened immune system.
Symptoms
Depending on the location of fibrillary astrocytoma, symptoms can be frequent, constant or paroxysmal:
- Convulsive syndrome. A fairly common general cerebral or focal symptom is the appearance of seizures. Over time, generalized attacks may occur with the appearance of visual or auditory hallucinations and loss of consciousness.
- Attacks of vomiting accompanied by severe headache . The cause of such attacks is irritation of the vomiting center of the brain. Possible dizziness, tinnitus, and weakness of the limbs.
- Vestibular disorders ─ loss of balance, reflex movements of the hands, disturbances in gait, statics and coordination.
- Mental disorders. The patient loses interest in life, becomes increasingly irritable, has mood lability, decreased intellectual skills, and slow thinking. Lethargy, dull attention and memory lapses, an unusual reaction to the usual environment should be alerted.
- Deterioration of hearing and vision.
- The appearance of high intracranial pressure in the presence of congestive processes in the fundus.
As fibrillary astrocytoma grows, it is accompanied by severe headaches. At an early stage of the disease, attacks usually occur in the morning or with a sudden change in head position. As the disease and intracranial hypertension progress, the pain becomes continuous and bursting.
Diagnostics
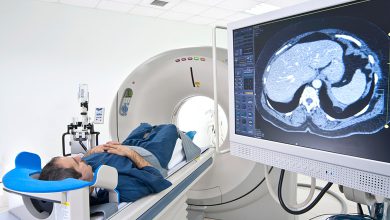
The first step in diagnosing fibrillary astrocytoma is a complete neurological examination based on the patient’s complaints. This method helps to identify brain pathology when assessing reflexes. For further examination, it is advisable to perform angiography and establish the source of nutrition of tumor tissues. The standard golden procedure for diagnosing fibrillary astrocytoma is MRI (can be done with contrast). Confirmation of the diagnosis is possible only after taking and confirming a histological sample of tumor tissue.
Treatment
Based on a diagnostic examination, taking into account the duration, course and picture of the disease, the doctor determines the further course of treatment. For fibrillary astrocytoma, radical surgery is performed in 85% of cases. During surgery, it is not always possible to completely remove the tumor. To reduce the risk of developing neurological deficits, radiation therapy with an emphasis on distant residual formations.
Please rate the article: