Pituitary adenocarcinoma - symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
The content of the article
Pituitary adenocarcinoma is a malignant neoplasm that has a destructive effect on the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland is an endocrine gland that produces many hormones that control the activity of almost all human systems and organs. For example, they directly and indirectly affect the regulation of metabolism, growth processes, and reproductive function. Naturally, any subtle interference in the above mechanisms leads to serious consequences that can threaten the patient’s life.
The pituitary gland contains the adenohypophysis (anterior lobe), which produces most of the substances that exhibit hormonal activity. This is where adenocarcinoma, growing from glandular cells, is most often detected. The tumor is characterized by rapid infiltrative growth, accompanied by damage to the pituitary gland and adjacent tissues. Adenocarcinoma quickly forms metastases. In this case, atypical tumor cells spread throughout the body through the blood or lymph flow. They are retained in other tissues and organs, which gives rise to new foci of tumor growth. Metastases can form both in the spinal cord and brain, and, for example, in the liver, bones, lungs (systemic metastases in internal organs).
Symptoms
The complex of symptoms is the same as for pituitary adenoma. Mainly observed:
— neurological disorders (severe pain in the head);
— hormonal imbalances (the amount of pituitary hormones increases);
- visual impairment (predominantly the temporal fields of vision are lost, ocular motility and muscle function are impaired, partial or complete blindness may occur).
Diagnostics
If pituitary adenocarcinoma is suspected, the following is performed:
— checking hormonal status;
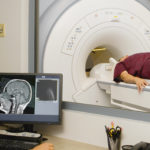
— MRI of the brain and/or MRI of the pituitary gland, which provide accurate information about the location of the tumor, its structure, shape, and blood supply characteristics.
In addition, these procedures allow us to draw a conclusion about how intensely the tumor interacts with surrounding tissues and optic nerves (that is, about the extent of the tumor process). If a malignant form is suspected, contrast is used. Based on the results of MRI with contrast, a conclusion is made about malignancy if it looks like a large, irregularly shaped formation with blurred, unclear boundaries and a heterogeneous structure.
Treatment
The main therapeutic measure to eliminate the tumor is its maximum surgical removal, after which radiation therapy .
The one-year survival rate after surgery is 50%, but survival rates of 3-4 years are common if the patient’s quality of life is high.
Other methods of treating pituitary adenocarcinoma are drug therapy, radiosurgery, and chemotherapy .
The Cyber-Knife installation, used during the treatment of adenocarcinoma, makes it possible to accurately direct high-dose ionizing radiation to tumor cells without damaging healthy tissue. This method is non-invasive, painless, eliminates postoperative complications and is implemented without anesthesia.
Please rate the article: