Pituitary adenoma (ICD code 10)
The content of the article
A tumor of the central endocrine gland - pituitary adenoma (ICD code 10) is most often found in patients with increased functional load of the organ, genetically predisposed to the disease, as well as in women.
Revealing
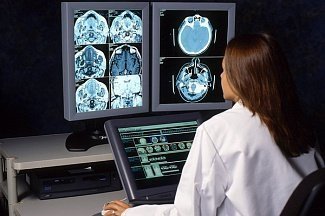
The formation can be detected during an imaging examination: during MRI of the brain, computed tomography, analysis of the patient’s hormonal levels, X-ray of the head (changes in the size and shape of the sella turcica), neuro-ophthalmological examination. In most cases, the tumor is detected by chance or during preventive procedures, since in the absence of hormonal activity the disease occurs without symptoms. Small adenomas cannot be detected visually; radioimmunoassay should be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Classification
By size they are distinguished:
- pituitary microadenoma (up to 10 mm in diameter);
- picoadenomas (pathological, up to 3 mm in diameter);
- giant adenomas (40 mm or more in diameter);
- macroadenomas (diameter from 10 to 40 mm).
Classification by histology. Pituitary adenoma occurs:
- chromophobic (presses nerve endings);
- acidophilus (somatropinoma);
- benign;
- basophilic (secreting, symptoms - Itsenko-Cushing syndrome);
- prolactinoma;
- adenocarcinoma (aggressively developing, metastases are observed);
- mixed tumors;
- thyroid-stimulating (rare);
- hormonally inactive.
Symptoms
The clinical manifestation of the disease pituitary adenoma (ICD code – 10) differs significantly in different patients depending on the type of neoplasm. Difficulty in identifying non-hormonal formations in the absence of symptoms. Hormonal tumors are manifested by various changes in the physical and microbiological parameters of the patient.
A small pituitary adenoma does not put pressure on adjacent tissues, there are no changes in vision, motor skills, or headaches. 20-30% of pituitary tumors are hormonally inactive, do not secrete, and patients have no apparent reason to consult a specialist.
The most active adenomas, prolactinomas, form in women. The hormone prolactin stimulates lactation, disrupts ovulation, and affects weight gain. In men, increased levels of the hormone are manifested by attacks of impotence and discharge from the mammary glands.
Pituitary microadenoma somatotropinoma manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- a sharp increase in height in children;
- acromegaly in adults (enlargement of the feet, hands, cheekbones, brow ridges, deepening of the voice). As a result, arterial hypertension, secondary diabetes mellitus, and the risk of developing cancer.
Experts assign the disease pituitary adenoma code according to ICD 10 . In adults, it is easier to determine the nature of the neoplasm than in children. Diagnosis of a child is complicated by an adequate response to research methods and the inability to explain and describe the symptoms of the disease.
Key symptoms to watch out for:
- deterioration of the field of vision;
- sudden weight gain;
- frequent urination;
- dizziness;
- intense headaches;
- dry skin;
- increased fatigue;
- depression;
- general weakness;
- apathy.
Consequences
A tumor diagnosed in the early stages can be easily cured promptly or surgically without any consequences for the patient’s body. An untimely detected adenoma can secrete, and there are cases of hemorrhage into the tumor. In this case, the patient feels nausea, dizziness, diplopia develops, and the patient may lose vision.
Treatment
For certain sizes and positions of the tumor, a more risky transcranial surgery may be prescribed.
Modern clinics offer radiotherapy to treat pituitary adenoma . During the operation, tissues are not damaged, the radiation is clearly directed, and the risk of impact on adjacent tissues is minimal.
Please rate the article: